Oceans support an immense diversity of life and ecosystems. From the warm tropical waters of the Caribbean to the freezing polar regions (and from tiny zooplankton to blue whales!), a staggering range of animals, plants and other life forms call the ocean their home. These ocean habitats (or marine habitats) provide everything needed for survival – food, shelter, water and oxygen. They need to be healthy in order to support the diversity of life within them and contribute to a healthy ocean, which provides us with many things including food, oxygen, jobs and a whole heap of fun water-based activities.
Types of Ocean Habitat
Marine habitats are divided into two main zones – coastal habitat and open ocean habitat. Within these habitats, there are numerous sub-habitats.
Coastal Habitats
 The coastal habitat is the region from the shoreline out to the continental shelf. Most marine creatures live in coastal habitat, although it only makes up seven percent of the ocean.
The coastal habitat is the region from the shoreline out to the continental shelf. Most marine creatures live in coastal habitat, although it only makes up seven percent of the ocean.
Coastal habitats include intertidal zones (constantly exposed and covered by the ocean’s tides). These include:
Rocky shore, mangrove, mudflats, estuaries, kelp forest, sea grass, sandy shores/beach and coral reefs – see below for more about these.
Open Ocean Habitats
 Open ocean habitats are found beyond the continental shelf. This is the deep ocean. Open ocean habitats are divided into layers which include: surface waters, the deep sea, and the ocean floor.
Open ocean habitats are found beyond the continental shelf. This is the deep ocean. Open ocean habitats are divided into layers which include: surface waters, the deep sea, and the ocean floor.
It is estimated that about 10 percent of marine species live in the open ocean. They tend to be the largest and fastest, such as whales and sharks, or fish that swim in schools. Tiny marine life such as plankton also inhabit this zone, which is often referred to as the pelagic zone – this simply means open ocean in Greek.
Food chains can be found in the open ocean: small bait fish eat plankton, bigger fish eat the bait fish, and sharks and some whales eat the bigger fish. Some whale species eat tiny plankton. In fact, the largest creature on earth, the blue whale, eats tiny plankton.
Some animals are able to travel to great depths but also spend much of their time close to the surface. The sperm whale can dive kilometers deep into the ocean, yet spends most of its time near the surface. Water temperatures vary greatly in this zone with the water being warmed by the sun near the surface and very cold deep down.
Coral Reef Habitat
Coral reef habitat consists of many single-living organisms (polyps) living together as one large mass. It comes in many different  shapes and forms. Coral reefs are responsible for a huge proportion of the earth’s biodiversity with an estimated 25 percent of all marine species living in and around them.
shapes and forms. Coral reefs are responsible for a huge proportion of the earth’s biodiversity with an estimated 25 percent of all marine species living in and around them.
Corals live with algae in a type of relationship called symbiosis. This is where two different species of organism interact or cooperate with each other. The algae, called zooxanthellae, live inside corals where they are protected by the coral’s tough outer shell. In return, the algae provide food for their host that they produce by the process of photosynthesis. Zooxanthellae is also responsible for the striking colours we often see in corals. Without these algae, corals become transparent, exposing their white skeleton. This is known as coral bleaching.
Coral reefs provide protection and are home to millions of marine creatures (as well as algae). They also act as nurseries for juvenile creatures and act as a barrier protecting land foreshores (the coastline), seagrass and other marine vegetation. So, in effect, they protect our home (habitat) too!
Coral is an essential part of the food chain and ecosystems, without it marine animals would perish – from sharks right down to the smallest algae.
Human Impact on Coral Reef Habitat
In order to thrive and support a healthy ecosystem, coral reef requires a moderate ocean temperature and clean water. Climate change is resulting in ocean temperatures rising and in many regions, the ocean is polluted. This is worrying scientists and citizens around the world. We can all play a part in helping to protect our oceans by doing simple things such as disposing of plastics carefully. Click here to find out how else you can help the ocean.
Mangrove Habitat
Mangroves are tough trees and shrubs that live in the coastal intertidal zone where they are able to survive in salty water.  They form extremely important habitats, providing protection for millions of marine animals as well as filtering and cleaning the water and the air, and protecting land from erosion.
They form extremely important habitats, providing protection for millions of marine animals as well as filtering and cleaning the water and the air, and protecting land from erosion.
Here are just a few of the benefits of mangrove habitat:
-Stabilize the coastline
-Protect water and air quality
-Reduce coastal flooding
-Provide habitat for fish
-Protect wildlife species
-Protect young fish from predators
-Serve as a nesting area for birds
-Protect species that humans rely on as a food source. It is estimated that 75% of commercial food caught has a direct link to mangroves!
Animals Commonly Found in Mangroves in Australia
Mud crabs, prawns, fiddler crabs, mangrove snails, molluscs and many species of fish, most common being the Mangrove Jack, Bream, Moses Perch, Whiting, Mullet & Flathead.
Wading birds: herons, pelicans, cormorants, curlews & egrets,
Rocky Shore Habitat
The rocky shore habitat comprises many microenvironments and ecosystems providing safe living habitat for a large diversity of  animals, including:
animals, including:
Molluscs: Oysters, limpets, chitons, barnacles, crustaceans: crabs, prawns, lobsters, echinoderms: sea Stars, sea cucumbers, sea urchins, many species of fish and some dangerous animals such as the blue-ringed octopus and the cone shell!
The rocky shore also acts as a nursery, protecting juvenile animals and enabling them to grow before venturing out to deeper, less protective areas of the ocean.
The food chain system of rocky shore environments can be divided into three groups: the producers, the grazers and the scavengers/predators.
Producers include algae and plankton which both produce energy through photosynthesis. They are at the bottom of the food chain. The grazers feed on the producers and include creatures such as mussels, limpets and sea cucumbers. Sea cucumbers are also scavengers as they sweep the sea floor for food, picking up small particles of both producers and grazers as they go. Crabs, fish, turtles, and even some species of shark, eat sea cucumbers – these are all examples of predators.
Sandy Beach Habitat
There are two main types of sand:
Mineral sand – weathered mineral rock)
Carbonate sand – weathered down rocks containing calcium from parts of  animals (eg. sea stars, coral fragments, bones of dolphins, whales & dugongs, sea urchins, crustacean & mollusc shells, fish & shark teeth).
animals (eg. sea stars, coral fragments, bones of dolphins, whales & dugongs, sea urchins, crustacean & mollusc shells, fish & shark teeth).
Sandy Beach is an important food zone linking the ocean to the land. Many small creatures live in this habitat, including worms and millions of microorganisms. Sandy Beach is also an important habitat for turtles to nest in and home to mammals such as rats and reptiles like snakes and lizards.
This zone provides a buffer zone, protecting land vegetation from ocean movement, wind and rain. Gentle tides may deposit sand onto beaches, while strong water movement, such as a storm, may erode sand from beaches. This means that beaches are changing all the time.
Seagrass Habitat
Seagrass is mainly found growing from mud or rock in bays, estuaries and coastal waters, and reaches a depth of up to 60  metres. it is the only flowering plant in the world that can live underwater. People often confuse sea grass with seaweed but seagrasses have roots, stems and leaves and produce flowers, fruits and seeds – seaweed does not!
metres. it is the only flowering plant in the world that can live underwater. People often confuse sea grass with seaweed but seagrasses have roots, stems and leaves and produce flowers, fruits and seeds – seaweed does not!
Seagrass is an important food source for large animals like turtles and dugongs as well as smaller creatures such as sea urchins and fish. It traps food to feed on and algae grow on its surface, providing food for water birds, molluscs and other dwellers. So, seagrass is an important energy pathway, supporting the food web in many ways.
Seagrass also acts as protection for juvenile animals that seek shelter in it.
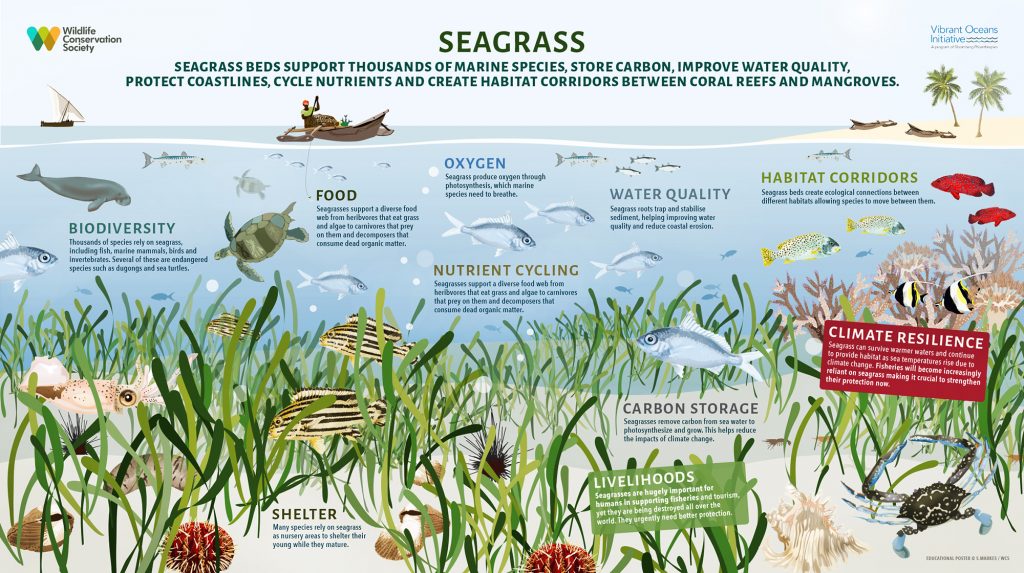
Copyright: Wildlife Conservation Society
Queensland’s Marine Habitats
 Queensland’s stunning coastline comprises a wide range of marine habitats. These include sandy and rocky shores, mangroves, and coral reefs; with the largest reef of all, The Great Barrier Reef, located just off Queensland’s coast.
Queensland’s stunning coastline comprises a wide range of marine habitats. These include sandy and rocky shores, mangroves, and coral reefs; with the largest reef of all, The Great Barrier Reef, located just off Queensland’s coast.
For more information on Queensland’s marine habitats, check out Ocean Life Education’s NEW Habitats video presented by our owner and Senior Marine Biologist, Richard Coward. Habitats video
To book a Habitats-themed incursion at your school of centre, go to our website:
Download FREE printable HABITATS FACT SHEETS


