Ocean Life Education’s Habitats Program
Ocean Life Education’s Habitats – Physical Conditions program elevates Year 6 students’ understanding of habitats by focusing on marine environments. Students will explore the specific physical conditions required for marine animals to survive and thrive. They will learn how changes to these conditions can negatively affect marine life, leading to poor health or even death. The program encourages discussions on strategies to prevent these harmful impacts in the future.
During our Habitats incursions, students will delve into a diverse range of physical conditions, including:
- Temperature
- Salinity
- Light
- Nutrients
- Current flow
- Waves
- Turbidity
- Depth

The Great Barrier Reef
Habitats Case Study: The Great Barrier Reef, Queensland
Our focus will be on Queensland’s coral reef habitat, particularly the Great Barrier Reef, the world’s largest fringing reef, located right at our doorstep. As one of the seven natural wonders of the world, it is essential to understand the physical conditions necessary for its survival so we can work to preserve it for the future.
What is Coral?

coral polyps
Though corals resemble plants on the ocean floor, they are actually marine animals related to jellyfish and sea anemones. Corals belong to the Cnidaria group, known for their stinging tentacles.
These invertebrates are colonial organisms, meaning many individuals live and grow connected in colonies. The Great Barrier Reef hosts around six hundred coral species which are made up of polyps, clear tube-like structures with stinging tentacles used for catching prey and defence.
Coral Reef Habitat – Necessities to Thrive
Temperature: Corals thrive in warm tropical waters, ideally between 23–29°C.
Salinity: They prefer salty conditions with salinity levels between 32–42 ppt.
Light: Sunlight is crucial for coral survival, as symbiotic algae within them need to photosynthesize to produce food.
Nutrients: Low nutrient levels are important to prevent smothering; calcium is essential for building coral skeletons.
Current Flow: Currents bring food, calcium, and disperse sediment, aiding in photosynthesis and coral spawn distribution.
Waves: Waves provide oxygen, food, and prevent sediment buildup on corals.
Turbidity: Low turbidity ensures sunlight penetration, crucial for coral survival.
Depth: Corals thrive in shallow waters, up to 70 meters, but prefer depths between the surface and 30 meters for optimal sunlight.
Human Impact

Coral Bleaching
Students will explore how human activities have altered the reef’s physical habitat and its effects on marine life. They will also discuss strategies to minimize negative impacts on the reef now and in the future.
Coral Bleaching
Climate change has raised water temperatures, especially in the northern Great Barrier Reef, surpassing 29°C and causing coral bleaching. Discussions will cover human actions like carbon pollution from cars and factories that accelerate climate change. Students will learn about coral bleaching, its causes, and potential prevention measures.
Land Clearing
The removal of trees and vegetation near coastal and river areas increases soil erosion, leading to sediment washing into oceans. This sediment smothers and kills coral. Students will investigate the effects of land clearing on marine environments.
Extension to Human Impact on the Ocean
Other human activities like plastic pollution and the use of shark nets and baited drum lines for shark control will be discussed. Students will learn about plastic’s harmful effects on marine life, particularly sea turtles.
The use of shark nets and drum lines since 1962, which results in unnecessary harm to marine animals, will be debated. The discussion will focus on modern, more effective technologies for protecting humans and marine life at beaches.
Ocean Life Education Habitats – 3 Minute Video
In this short film, Ocean Life Education’s Director of Education, Richard Coward, highlights key Habitats learning points using our marine animals as examples. It’s a great precursor to an incursion, which can be watched with students as a quick taster and talking point in advance of our visit.
A Note About Year 6 Curriculum Science
This incursion aligns with the Australian Curriculum content description ‘Science Understanding’ under the sub strand of ‘Biological Science’ for year 6’…
The growth and survival of living things are affected by physical conditions of their environment.
Creating Ocean Advocates
At Ocean Life Education, we believe people protect what they know and love. Our mission is to inspire a deep connection to the ocean in children through engaging science incursions. By creating hands-on, memorable experiences, we aim to spark a lifelong passion for marine conservation and the ocean’s wonders.
Useful links
Overview of Marine Habitats
Habitats Fact Sheets
Other Primary Resources
Our Primary Incursions



 marine animal exhibit session, in order to maximise on beach time and find as many wildlife remnant treasures as possible!
marine animal exhibit session, in order to maximise on beach time and find as many wildlife remnant treasures as possible!
 including their key role in ocean food chains and how they keep the ocean healthy by eating sick or dead animals and keeping numbers of other ocean dwellers in check.
including their key role in ocean food chains and how they keep the ocean healthy by eating sick or dead animals and keeping numbers of other ocean dwellers in check.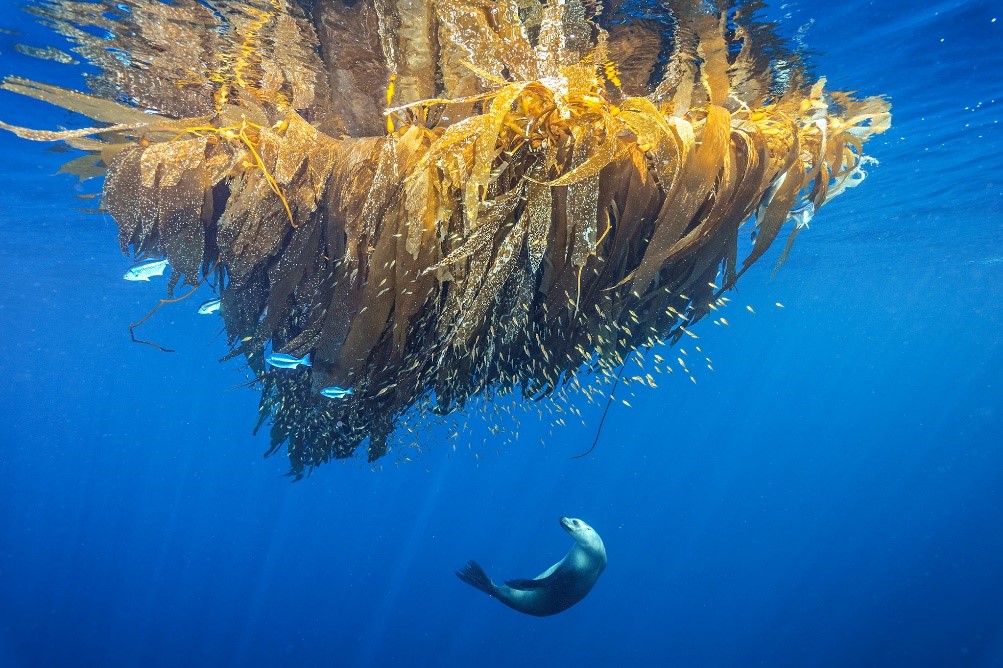


 shapes and forms. Coral reefs are responsible for a huge proportion of the earth’s biodiversity with an estimated 25 percent of all marine species living in and around them.
shapes and forms. Coral reefs are responsible for a huge proportion of the earth’s biodiversity with an estimated 25 percent of all marine species living in and around them. They form extremely important habitats, providing protection for millions of marine animals as well as filtering and cleaning the water and the air, and protecting land from erosion.
They form extremely important habitats, providing protection for millions of marine animals as well as filtering and cleaning the water and the air, and protecting land from erosion. animals, including:
animals, including: animals (eg. sea stars, coral fragments, bones of dolphins, whales & dugongs, sea urchins, crustacean & mollusc shells, fish & shark teeth).
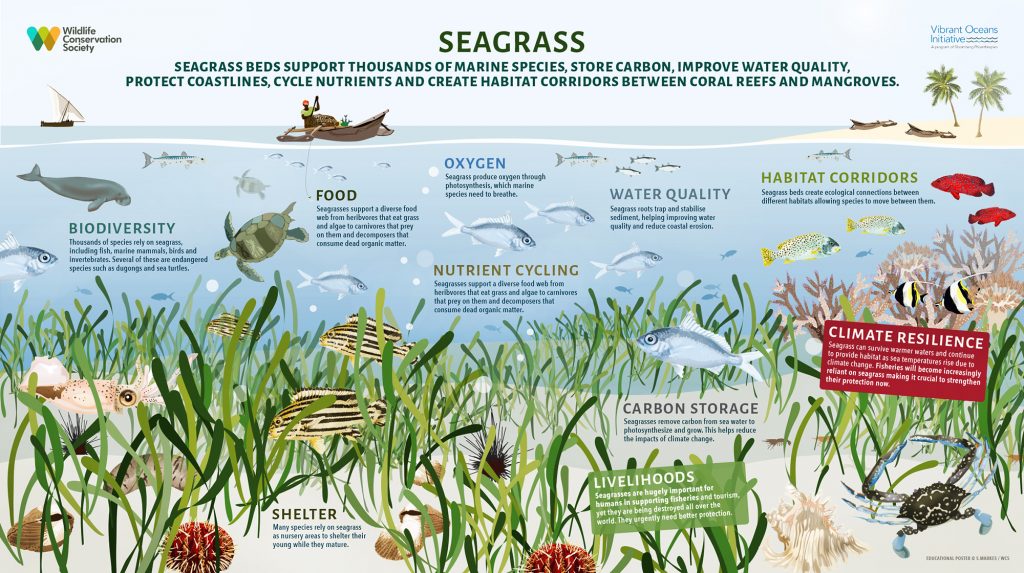
animals (eg. sea stars, coral fragments, bones of dolphins, whales & dugongs, sea urchins, crustacean & mollusc shells, fish & shark teeth). metres. it is the only flowering plant in the world that can live underwater. People often confuse sea grass with seaweed but seagrasses have roots, stems and leaves and produce flowers, fruits and seeds – seaweed does not!
metres. it is the only flowering plant in the world that can live underwater. People often confuse sea grass with seaweed but seagrasses have roots, stems and leaves and produce flowers, fruits and seeds – seaweed does not!